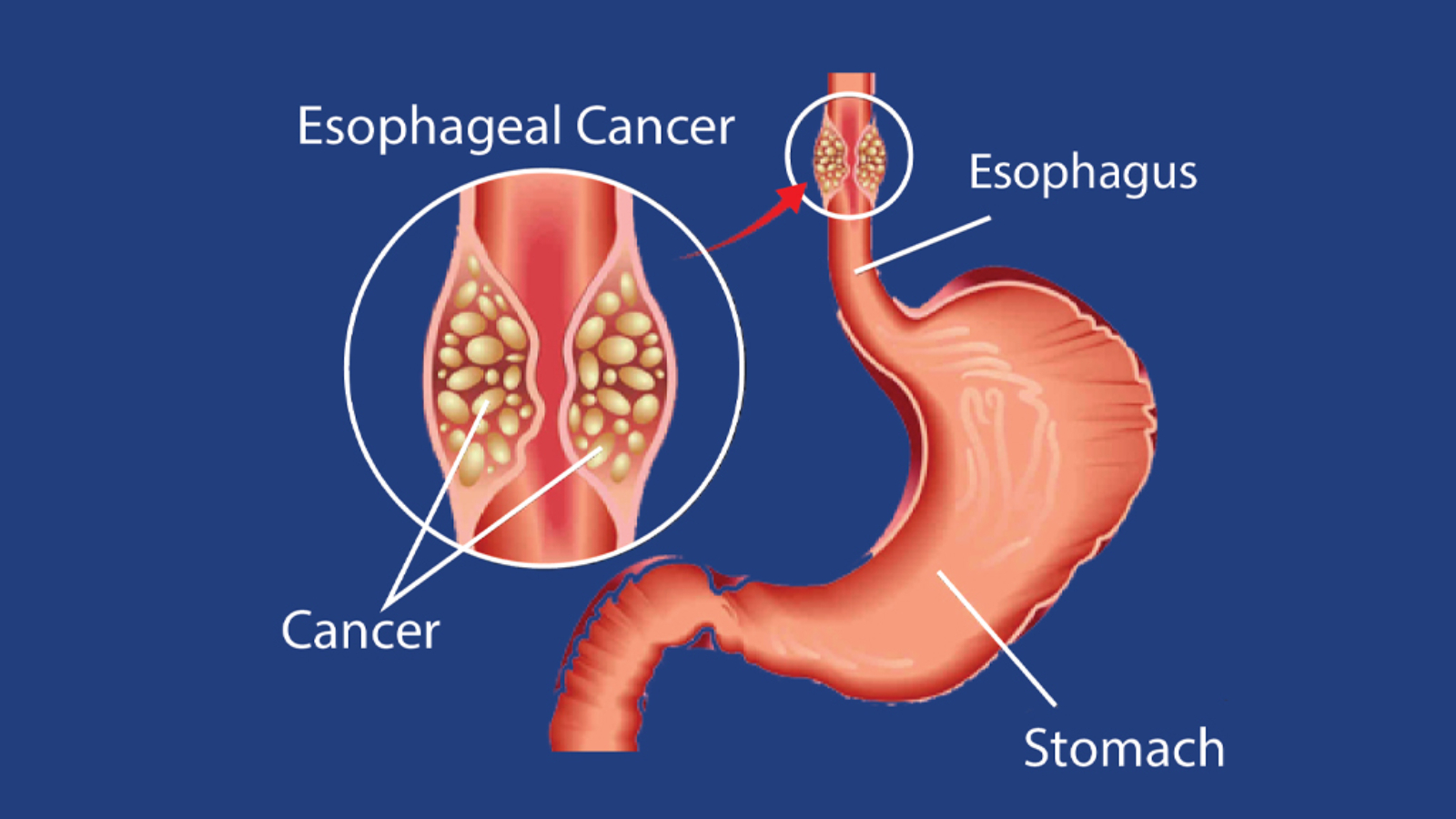
Esophageal Cancer is a condition when cancerous cells develop in the esophagus, which is the tube-like structure that runs from your throat down to your stomach. Cancer begins at the inner layer and can spread throughout the layers of the esophagus, also affecting other parts of your body. During the early stages, you might find it difficult to diagnose this type of cancer. However, understanding it in a comprehensive manner will help you manage the condition better. This blog will cover all the relatable aspects about Esophageal Cancer, along with its symptoms, causes and treatment options.
Esophageal Cancer Overview
Esophageal cancer is one of India’s most common cancers. The esophageal tumor primarily develops in the inner lining of the esophagus that can spread outward gradually to other layers or inwards towards the lumen as well as to nearby organs and lymph nodes.
Patients with esophageal cancer often experience swallowing problems, chest pain, bloody cough, blood in vomit, chest burn, indigestion and weight loss. However, it can occur in any age group, the risk of esophageal cancer is higher for people aged 45 and older.
During the early stages of esophageal cancer, you might not feel symptoms associated with this type of cancer. Once the symptoms appear, the disease progresses quickly and therefore, it becomes important not to ignore any symptoms.
Esophageal Cancer Types
Mentioned below are the two forms of Esophagus cancer:
- Adenocarcinoma: A condition that mostly occurs in the lower portion of the esophagus.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A condition that usually starts in the middle and upper part of the esophagus.
Signs and Symptoms
Listed below are a few symptoms associated with Esophageal Cancer:
- difficult or painful swallowing
- new heartburn
- reflux that doesn’t go away
- vomit that has blood in it
- black or bloody stools
- unexplained fatigue
- feeling of choking when swallowing
- feeling of discomfort in the upper abdomen
- unexplained weight loss.
Esophageal Cancer Stages
Since the esophageal cancer stage depends on the location, spread and tissues involved, listed below are the stages of this cancer:
Stage 0: This is the most initial stage of this cancer where the presence of abnormal cells in the esophageal inner lining is not cancerous.
Stage I: The presence of cancerous cells on the inner lining esophagus
Stage II: Cancer has spread to the outer layer of the esophagus, affecting one-two lymph nodes.
Stage III: Cancer spreads to deeper tissues, nearby organs and other tissues.
Stage IV: This is the most advanced stage of esophageal cancer that can spread to distant organs.
What is the impact of esophageal cancer on my body?
This type of cancer occurs when cancerous cells multiply in the esophageal tissues, eventually forming a tumor. Esophageal Cancer is aggressive but most people do not notice symptoms until the cancer has spread. Your esophagus expands to accommodate large things like big bites of food. The tumor starts to grow and block the opening of your esophagus and you may find it difficult to swallow or feel pain, often starting like need of water to swallow down the solid food and slowly increasing, so it becomes difficult to even swallow the water.
Risk Factors
Listed below are a few risk factors that may increase the chances of developing Esophageal Cancer:
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Obesity or being overweight
- Tissue changes in your vocal cords due to HPV
- Barrett’s esophagus and chronic acid reflux
- Neck or head cancer history
- Exposure to chemicals
- Inherited disorders like achalasia or tylosis
Esophageal Cancer Diagnosis
If you notice any of the above-mentioned symptoms, the doctor will begin by analyzing your medical history. After this, your doctor may recommend a few diagnostic tests listed below:
Barium swallow: This is a kind of X-ray where you will be asked to drink a liquid with barium to make your food pipe easily visible to the doctor.
CT Scan: A computed tomography scan that lets your doctor determine if the tumour has spread to the chest or abdomen (belly).
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD): Doctors use an endoscope, a long, thick tube with camera at the end to visualise and check for abnormalities within your food pipe.
Esophageal endoscopic ultrasound: In this process, doctors use sound waves to create an image of the esophagus.
Biopsy: The expert will remove a small amount of abnormal esophageal tissues during the endoscopy to check for cancerous cells.
Esophageal Cancer Treatment Options
Surgical Methods
Esophagectomy: Under this treatment, the surgeon will remove a portion of your esophagus, along with the tissues surrounding it. The surgeon then creates a new food tube by pulling a portion of your stomach up into your chest, and combining it with the remaining esophagus.
Endoscopic submucosal dissection: This procedure is used to treat esophageal cancer in its very early stages.
Endoscopic mucosal resection: The doctors prefer this to remove tumors from the mucous layer of your esophagus.
Adjuvant Therapies
Chemotherapy: A treatment that is usually administered intravenously or as an oral therapy, uses drugs to slow or stop the growth of cancerous cells. Combining chemotherapy with other treatments can be helpful to treat esophageal cancer.
Targeted Therapy: This therapy involves certain drugs to target cancer cells and stop their spread.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-powered energy pulses such as X rays or proton beams to kill cancerous cells.
Immunotherapy: This treatment involves boosting the immune system to combat cancer cells. Immunotherapy boosts the production of cancer-fighting immune cells in your body or helps healthy cells to identify and attack cancerous cells.
Endoscopic Laser Therapy: The treatment of esophageal carcinoma is usually performed using laser light delivered by an endoscope.
Prevention of Esophageal Cancer
Primary Prevention
Listed below are a few primary prevention methods that involves identifying and reducing the risk factors for esophageal cancer:
- Stop smoking: Since smoking is associated with esophageal carcinoma, stop smoking and using other tobacco products.
- Limit your alcohol consumption: Reduce alcohol consumption as it may increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Changes in diet: Fill your diet with more fruits and vegetables rich in phytochemicals and antioxidants and avoid canned or frozen food.
- Maintain healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can help manage obesity, while reducing the risk of esophageal cancer and its associated complications.
Secondary Prevention
Such prevention methods include:
Regular Follow-ups: Based on your schedule, medical follow-ups are necessary to determine the extent of recovery, the risk of recurrence and the overall well-being.
Symptoms: Seek immediate medical attention if you notice any symptoms of complications or recurrence.
Lifestyle: Maintaining a regular exercise regime with a balanced diet can drive you towards a healthy lifestyle.
Control weight and diabetes: Diabetes, obesity and weight management are other ways to reduce the risk of complications.
Awareness: It is important to be aware of the condition and realistically accept it which will help you manage the condition better.
Wrapping Up!
We tried our best to cover all the relatable aspects that a patient must know about Esophageal Cancer. We discussed the condition in a comprehensive way to help our patients better understand and manage the condition. If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above, immediately see a cancer specialist at Samsara Cancer Care.
Patients can have personalized and compassionate care with the involvement of the top-rated doctors in our cancer care clinic. Dr. Sameeksha at Samsara Cancer Care is an experienced oncologist with a proven record in treating Esophageal Cancer. Being a top-rated medical expert, she ensures fully-informed and comfortable treatment to all her patients.