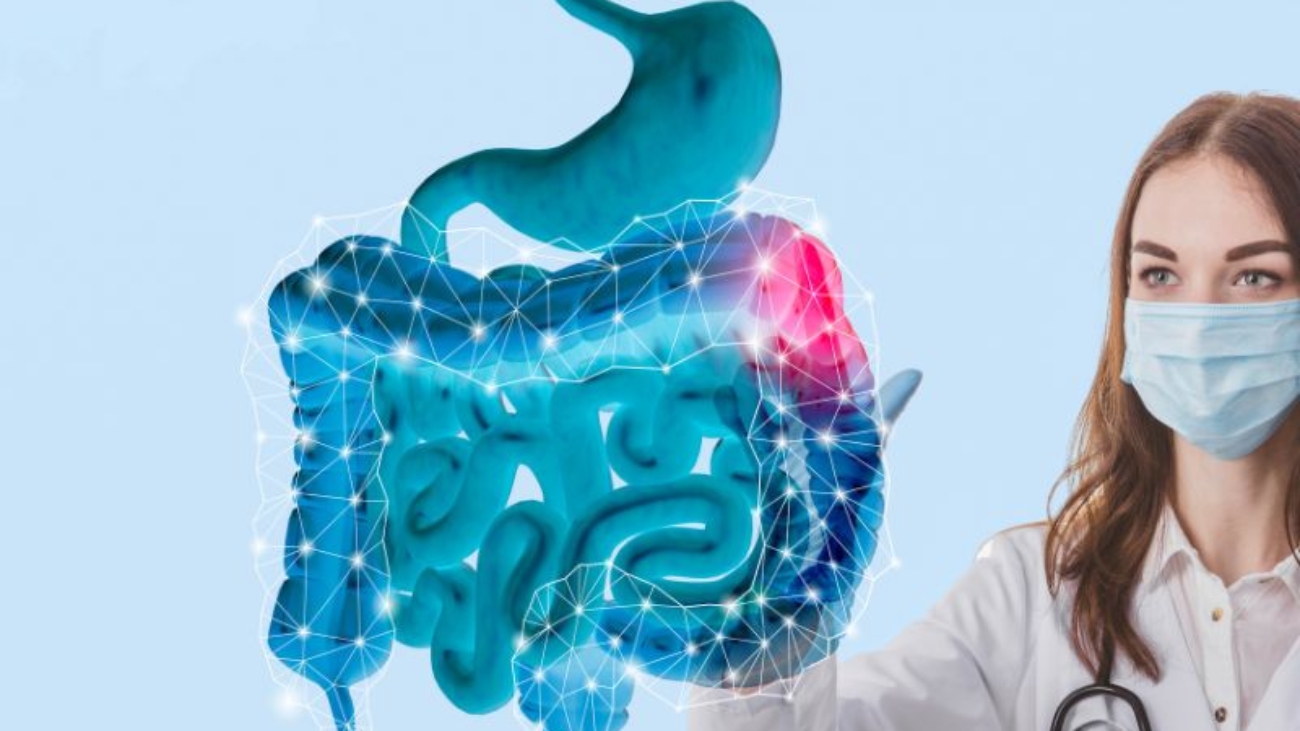
A very common form of cancer that usually begins as polyps (growths) in the colon’s lining. Through the diagnostic tests and appropriate treatment techniques, the medical specialists can identify and eliminate cancerous polyps. Categorized among the most prevalent cancer kinds, if not treated well, colon cancer can spread to other parts of the body that can worsen the body condition. With the tests for early detection and applying innovative treatments, the death risks from this kind of cancer are reduced. Certain types of polyps may transform into cancer with time, however, but not all polyps will become cancerous.
Understanding Colorectal or Colon Cancer
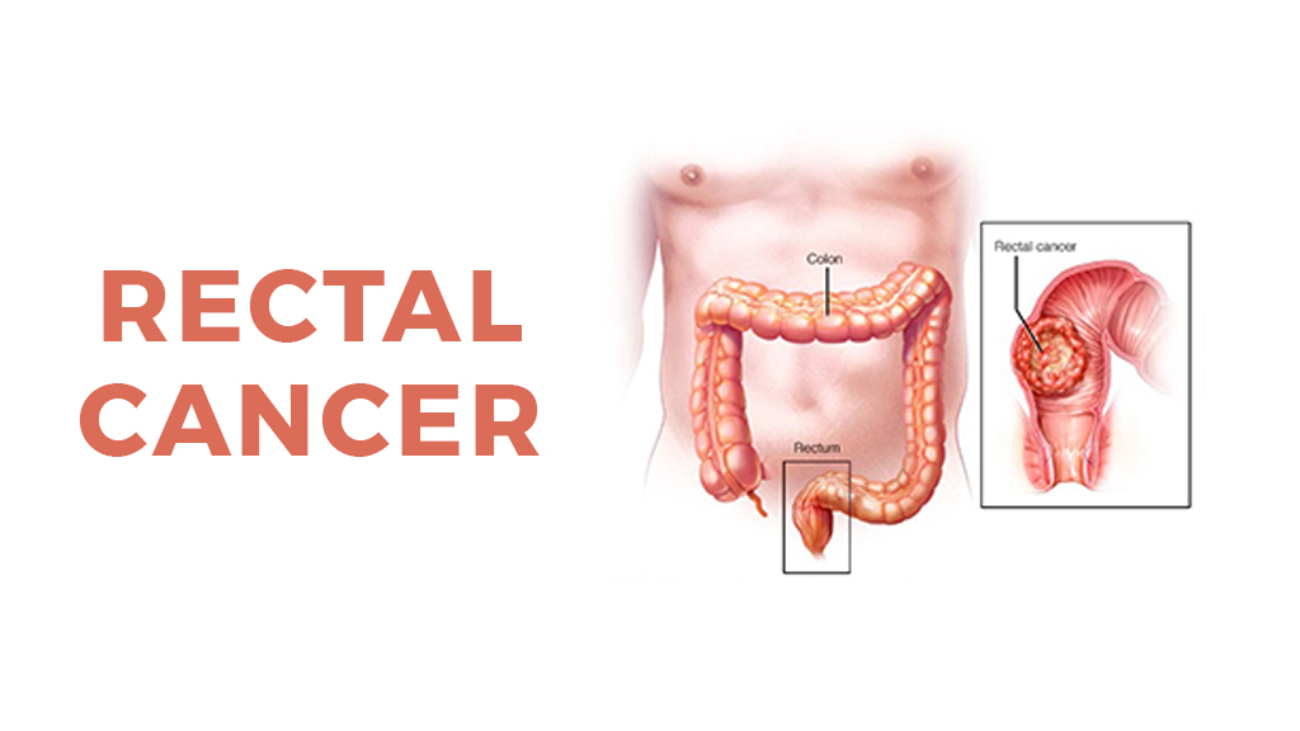
We can describe Colon Cancer as a type of cancer that usually begins in the colon (large intestinal tract), the long tube that carries digested food to your rectum, and then out of your body. Basically, colorectal cancer is a result of specific polyps or tumors that grow through the colon’s lining. The doctors usually suggest screening tests to detect precancerous polyps before they turn into malignant growths. Essentially, the Colorectal Cancer that isn’t detected or treated could result in spreading to other parts of the body. Proper screening tests for early detection and an appropriate treatment lowers the risk of death from colon cancer.
Colon Cancer Stages
After the patient undergoes the colon cancer diagnosis, the doctor may suggest some additional tests to determine the severity of the tumor, which is termed as the cancer stage. Considering the stage of the cancer developed in the patient’s body is necessary to prepare for the treatment strategy.
The staging tests may include the scans of the pelvis, abdomen and chest. Through the imaging tests, the doctors may capture images from the inside of your body and analyze them to find the actual location and size of the tumor. However, in some severe cases, the doctor may even require surgery procedures to determine the cancer stage.
Talking about the Colon cancer stages, it usually varies between 0 and 4, where the lowest number indicates that the cancer is confined to the colon’s lining. However, stage 4 depicts the spread of the disease to different parts within the body. To curb the disease spread, we advise all our readers to seek medical assistance without delays, if they face any colon cancer symptoms.
Risk Factors
Listed below are few risk factors that can lead to colorectal cancer in a human body:
Cancer In Family History:
Having a blood relation with someone who was diagnosed by colon cancer increases the chance of developing colon cancer.
Personal History of Polyps:
The presence of colon polyps already in the body may increase the chance of developing colon cancer.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease:
Conditions causing pain or an increase in the size of the stomach can cause inflammatory bowel disorders as this may increase the chance of developing colon cancer.
Genetic Disorders:
Certain DNA mutations increase the chance of developing colon cancer as the most frequent inherited disorders increase the risk of colon cancer.
Other Factors
- Not Exercising Regularly
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Processed meat consumption
Common Symptoms
Listed down here are a few symptoms that a person may commonly suffer if they have this illness:
Blood while passing stool:
The person must immediately seek medical help if they find blood while passing stool. However, not necessarily the presence of blood in poop indicates you’re suffering from colon cancer, other factors like hemorrhoids, anal tears and eating beets, may make your poop appear different. However, it’s best to speak with a health doctor whenever you notice blood on or in your stool.
Consistent change in your bowel habits:
If a person suffers from frequent constipation or diarrhea or feels like visiting a bathroom after having gone already, then advise you for medical assistance immediately.
Abdominal Discomfort:
Since pain in your belly area can trigger because of numerous reasons, but if the pain isn’t going away or becomes unbearable, speak to a physician if you notice such discomfort.
Bloated Stomach:
There are numerous factors that cause you to feel bloated, but if your belly feels bloated for longer than two weeks, consulting a doctor immediately is recommended before the situation gets worse.
Others:
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Vomiting
- Weakness or tiredness
- Fatigue and feeling short of breath
- decreased appetite
- constipation
- diarrhea
Diagnosis
Listed below are the Colon Cancer diagnosis procedures that your doctor may follow to understand the nature of the tumor:
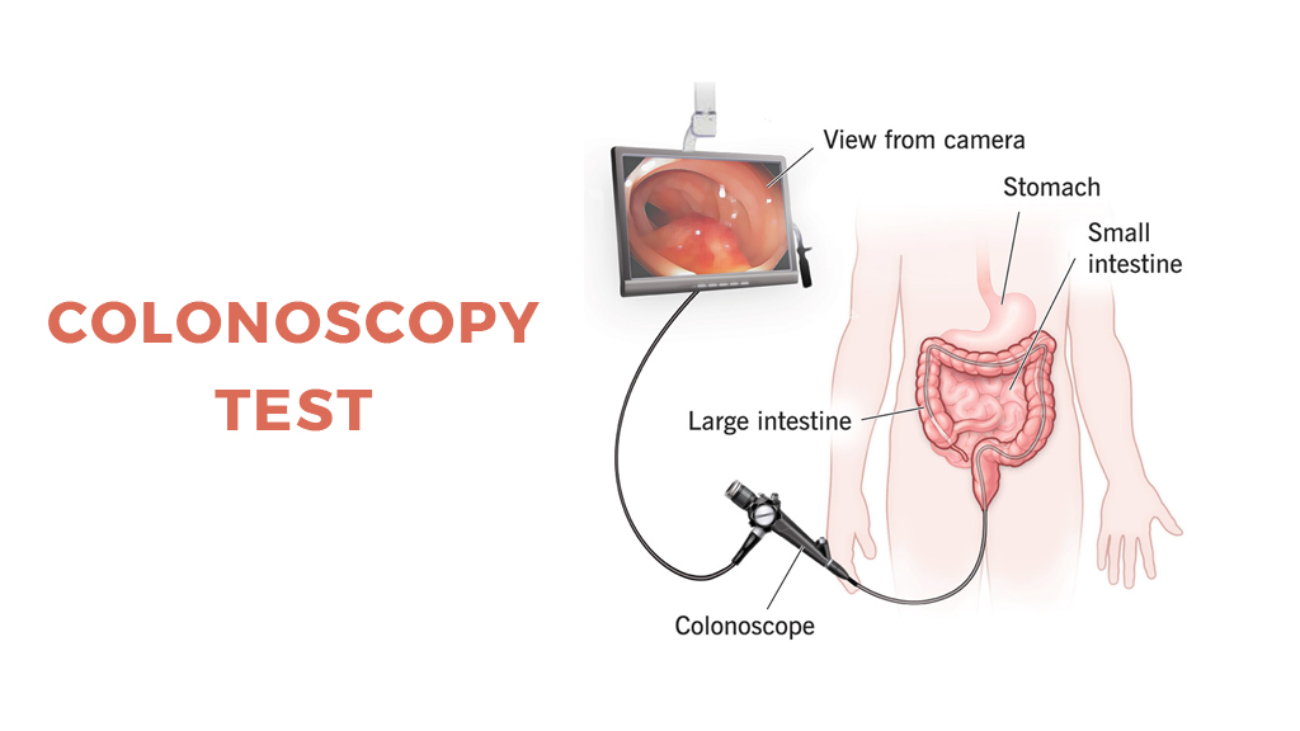
Using scope to analyze the colon:
Colonoscopy employs a long flexible and slender tube connected to an electronic camera and a monitor that provides a clear vision of the entire colon and the rectum. Using some surgical instruments, the doctors can take tissue samples to remove polyps.
Removal of a sample tissue to test:
The doctors follow a biopsy method to take a sample of tissue to analyze its status. The lab tests can reveal whether they are in fact cancerous as well as how fast they are expanding, however, other tests can provide additional details about the cancerous cells. The results will let the doctor analyze the prognosis of your case and formulate an appropriate treatment strategy.
Blood Tests:
The blood tests are done by the doctors to gather the details about the patient’s general health, including the liver and kidney function or even determining the decrease in red blood cells.
Treatment Options
Mentioned below are some of the treatment options that a doctor will suggest you if you are diagnosed with colon cancer.
Surgery
The doctors may use surgical methods to remove cancerous parts of the bowel and based on the severity of the procedure, the two sides of the bowel can be stitched to each other. If the tumor is present on the lower part of the rectum, then there might not be enough bowel remaining to connect and the situation demands for colonostomy.
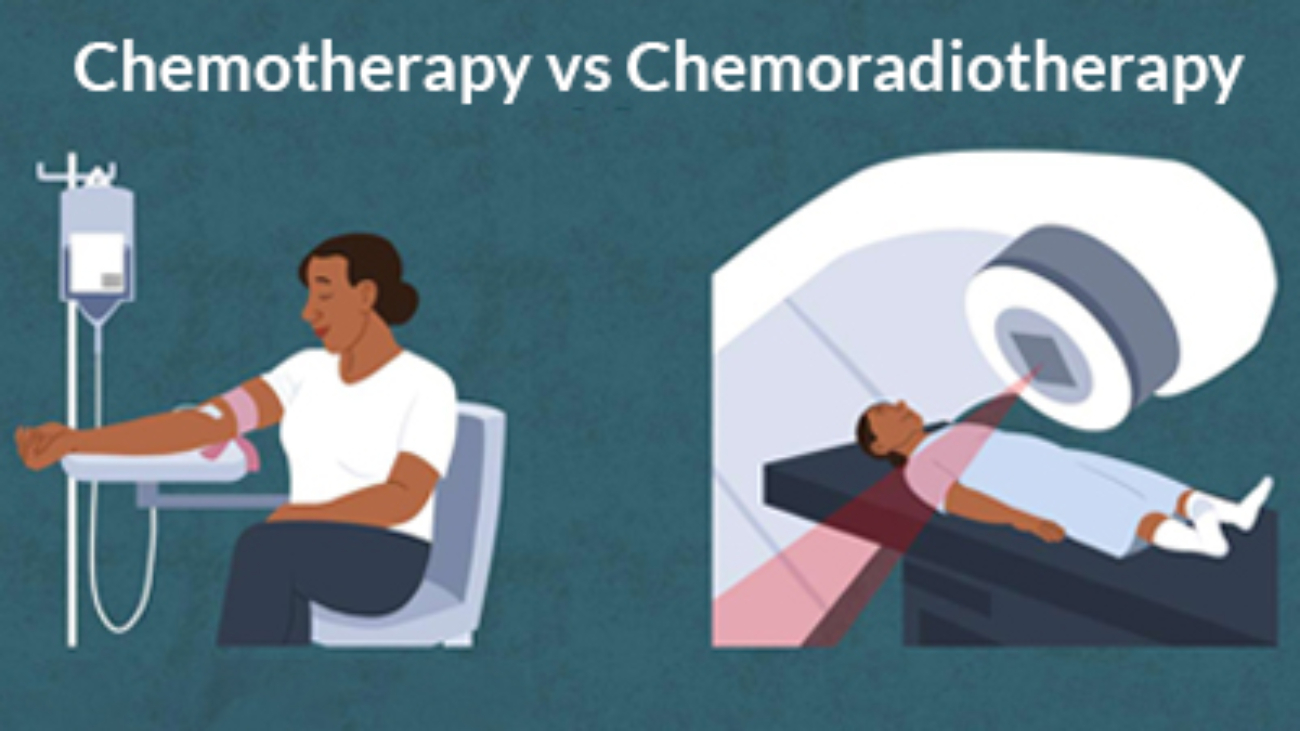
Chemotherapy
Another therapy involves chemotherapy which describes a treatment with anti-cancer medications, prescribed to destroy or stop cancerous cells by destroying their cells so that they don’t expand and divide.
Radiotherapy
As the treatment employs X-rays with high energy, it is designed specifically for you to ensure that the cancerous cells are destroyed in the minimal amount of harm on normal tissue. This is mainly used in Rectal cancer treatment.
Lifestyle Changes For Prevention
To prevent any such illness from trapping you, we advise you to make a little lifestyle changes in your routine as we mentioned below:
- In essence, you should try to maintain an appropriate weight that will lower the risk of developing other illnesses also. Talk to your physician about what a healthy weight you should be at.
- Regularly exercising for around twenty minutes is recommended every day to prevent yourself from becoming cancerous.
- Making healthy choices in your eating is another way to improve general health. But, there isn’t one specific diet you should adhere to beat cancer, however discussing your diet with your doctor could benefit you greatly.
- Stop making negative lifestyle choices and quit smoking tobacco. If you’re a cigarette smoker, you should visit your doctor to help you establish a plan to stop smoking and kick the habit.
- Recommended to avoid processed red meat and alcohol consumption.
- In case of any chronic disease like inflammatory bowel disease, continue monitoring and treatment
SCREENING GUIDELINES FOR COLORECTAL CANCERS
Screening guidelines for colorectal cancer typically vary depending on the recommending organization and the individual’s risk factors. However, there are some general guidelines that are commonly followed:
Age to Start Screening: Screening for colorectal cancer usually begins at age 45 for individuals at average risk, although some guidelines previously recommended starting at age 50. However, those with certain risk factors, such as a family history of colorectal cancer or certain genetic syndromes, may need to start screening earlier.
Screening Methods: There are several screening methods available for colorectal cancer. These include:
Colonoscopy: This is considered the gold standard for colorectal cancer screening. It involves the insertion of a flexible tube with a camera into the colon to look for abnormalities or polyps.
Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT): This test checks for blood in the stool, which can be a sign of colorectal cancer. It is done by collecting a stool sample at home and sending it to a lab for analysis.
Stool DNA Test (sDNA): This test looks for certain DNA markers in the stool that may indicate the presence of colorectal cancer or precancerous polyps.
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy: Similar to a colonoscopy, but only examines the lower part of the colon.
Virtual Colonoscopy (CT Colonography): This is a non-invasive imaging test that uses CT scans to create images of the colon and rectum.
Frequency of Screening: The frequency of screening depends on the method used and the individual’s risk factors. For example:
Colonoscopy is usually recommended every 10 years for average-risk individuals.
FIT is typically done annually.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy may be done every 5 years.
Virtual colonoscopy may be done every 5 years.
Follow-Up: If abnormalities or polyps are found during screening, follow-up procedures such as biopsies or polyp removal may be necessary. The follow-up frequency depends on the findings and the individual’s risk factors.
Conclusion
Since we tried our best to cover every relatable aspect about Colon Cancer for our readers, visiting a reputable medical facility for treatment can help you get a better understanding of the disease. To get individualised guidance and to discuss your symptoms, speak to Dr. Sameeksha Dubey renowned oncologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating Colon Cancer Treatment in Nagpur. With years of expertise treating such medical situations, she is an expert in examining and identifying the primary causes and providing comfort treatment to the sufferer. Book an appointment today!